Wrist and Hand Examination: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (link to existing pp pages, correct texts, deleted texts after references) |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== | == Introduction == | ||
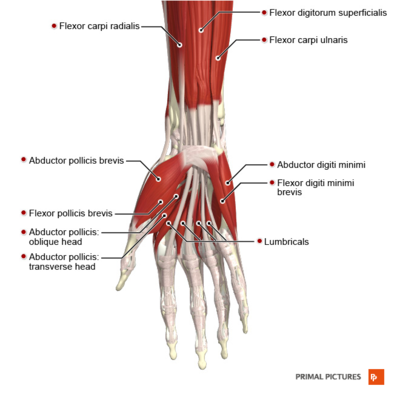
[[File:Muscles of the hand anterior aspect Primal.png|right|frameless|400x400px]] | |||
The hand and wrist form a group of complex, delicately balanced joints which are considered the most active portion of the upper extremity. Optimal overall function is important to so many activities of daily living. A hand and wrist examination done in a structured manner will help to facilitate the most appropriate working diagnosis for treatment. Diagnosing hand and wrist conditions is often difficult and for this reason, bilateral comparison can be useful<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Subjective History == | |||
Thorough history taking is an important first step in treating the patient. Each physical therapist will develop their own style and technique, but a good interview will include the basic elements discussed below: | |||
* Mechanism of the injury - How the injury occurred and what was the cause e.g. fall on an outstretched hand | |||
* Insidious or sudden injury. | |||
* Handedness, occupation, previous injury and fracture history | |||
* Location of the [[Pain Assessment|pain]] | |||
* Presence and location of numbness, pins and needles and/or tingling. | |||
* Aggravating and relieving factors. | |||
* Functional limitations. | |||
* Were any diagnostic test/imaging performed and what were the results? | |||
{{#ev:youtube|sypBEG9F6uU}} | |||
== <u></u>Objective == | == <u></u>Objective Examination == | ||
=== Screen Proximal Joints === | |||
Screen proximal structures to determine if they are involved in the patient’s clinical presentation. i.e. [[Cervical Anatomy|Cervical joints]], [[Shoulder|Shoulder,]] [[Elbow]]. | |||
=== Observation === | === Observation === | ||
Start by watching this 8 minute video of a wrist and hand examination. | |||
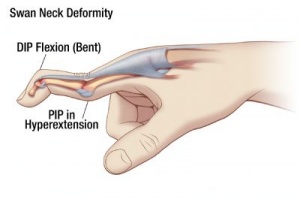
{{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DxW0rodKOGs|width}}<ref>Ascension Via Christi Joint-by-Joint Musculoskeletal Physical Exam: Hand and Wrist Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DxW0rodKOGs (last accessed 29.3.2020)</ref>[[File:Swan-neck deformity.jpg|right|frameless]] | |||
* Observe upper extremity as the patient enters the room | |||
*# Examine hand in function | |||
*# Deformities | |||
*# Attitude of the hand | |||
* Palmar Surface | |||
*# Creases | |||
*# [[Thenar and Hypothenar Muscles Of The Hand|Thenar and Hypothenar]] Eminence | |||
*# Arched Framework | |||
*# Hills and Valleys | |||
* Dorsal surface | |||
*# Hills and Valleys | |||
*# Height of metacarpal heads | |||
*# Deformities. | |||
* | * Ganglions - Cystic structure that arises from synovial sheath | ||
* [[Boutonniere Deformity|Boutonniere]] Deformity | |||
* | * [[Swan-Neck Deformity|Swan Neck]] Deformity (see image) | ||
* [[Wrist and Hand Osteoarthritis|Osteoarthritis]] - Heberden’s nodes: DIP, Bouchard’s nodes: PIP | |||
* [[Dupuytren’s Contracture|Dupuytren’s]] Contractures | |||
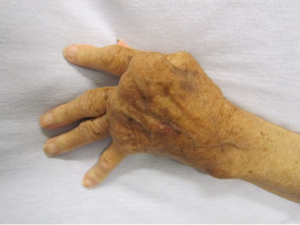
* | * [[Hand Rheumatoid Arthritis|Rheumatoid Arthritis]] - MCP swelling, Swan neck deformities, Ulnar deviation at MCP joints, Nodules along tendon sheaths.<ref name=":0">Shane Cass, DO UNM Primary Care Sports Medicine [http://unmfm.pbworks.com/w/file/fetch/50237999/HandandWristExammaster.pdf Clinical Examination of the Hand and Wrist Available] from:http://unmfm.pbworks.com/w/file/fetch/50237999/HandandWristExammaster.pdf</ref> (see R) | ||
#[[ | * Muscle wasting due to nerve dysfunction | ||
*#[[Median Nerve]] (depending on area impingement) | |||
[ | * Muscle wasting in the thenar eminence, first three fingers, and half the fourth fingers on radial side of the hand. | ||
*#[[Radial nerve|Radial Nerve]] (depending on area of impingement) | |||
*Muscle wasting in the hand for the ulnar nerve occurs primarily in the fifth and half the fourth fingers, in the hypothenar area. | * Common muscles that are affected by radial nerve entrapment are primarily on the dorsal aspect of the hand. | ||
*# [http://www.physio-pedia.com/index.php5?title=Ulnar_Nerve_Entrapment Ulnar Nerve (depending on area of impingement)] | |||
*# Muscle wasting in the hand for the ulnar nerve occurs primarily in the fifth and half the fourth fingers, in the hypothenar area. [[File:RA Hand 2.png|right|frameless]] | |||
=== Functional Tests === | |||
Goals - to obtain and quantify an asterisk to assess/reassess after the intervention is performed, for example: turning doorknob, holding a key, initial pain-free grip or key grip, opening a jar, turning on tap, lifting saucepan. [[Grip Strength|Grip strength]] can also be a good reliable tool to use (available cheaply on internet). | |||
< | === Palpation === | ||
'''Wrist (Dorsal to Volar)''' | |||
* Radial Styloid | |||
* [[Scaphoid]] | |||
* 1st MC/Trapezium joints | |||
* [[Lunate]] | |||
* Lister’s Tubercle | |||
* Ulnar Styloid | |||
* [[Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Injuries|TFCC]] | |||
* Triquetrum | |||
* [[Pisiform]] | |||
* Hook of [[Hamate]] | |||
* Guyon’s Tunnel<ref name=":0" /> | |||
'''Palpation of Hand''' | |||
* [[Bone]] | |||
** Metacarpals - 5, Phalanges - 14, (Palpate for swelling, tenderness) | |||
* Soft tissues | |||
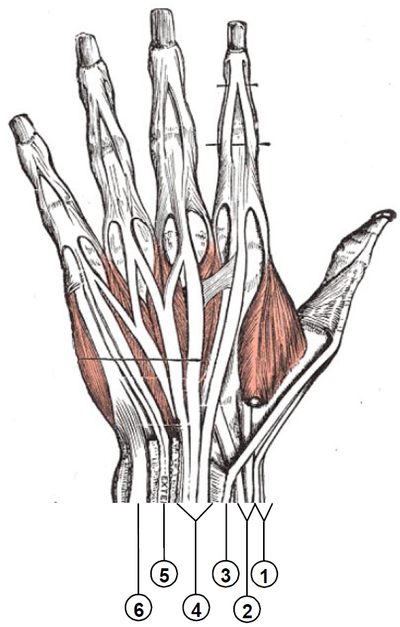
** 6 Dorsal Compartments – Transport extensor tendons See image at R | |||
1st compartment- [[De Quervain's Tenosynovitis|De quervains]] 2nd compartment - [[Intersection Syndrome|Intersection syndrome]] | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
!Compartment 1 (Most radial) | |||
!Compartment 2 | |||
!Compartment 3 | |||
!Compartment 4 | |||
!Compartment 5 | |||
!Compartment 6 (Most ulnar) | |||
|- | |||
|Abductor pollicis longus | |||
|Extensor carpi radialis longus | |||
|Extensor pollicis longus | |||
|Extensor indicis | |||
|Extensor digiti minimi | |||
|Extensor carpi ulnaris | |||
|- | |||
|Extensor pollicis brevis | |||
|Extensor carpi radialis brevis | |||
| | |||
|Extensor digitorum communis | |||
|} | |||
<ref>Wikimedia commons Wrist extensor compartments Available from:https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Wrist_extensor_compartments_(numbered).PNG</ref> | |||
2 Palmar Tunnels – Transport nerves, arteries, flexor tendons | |||
'''Palmar Aspect''' - Pisiform and Hamate, Tunnel of Guyon, Carpal Tunnel, Flexor Carpi Radialis, Flexor Carpi Ulnaris | |||
'''Palm of Hand''' | |||
* Thenar Eminence (3 muscles of thumb, Atrophy seen in carpal tunnel syndrome) | |||
* Hypothenar Eminance (3 muscles of little finger, Atrophy with ulnar nerve compression) | |||
* Palmar Aponeurosis (Dupuytren’s Contracture)<ref name=":0" /><br>[[File:Wrist extensor compartments (numbered).png|right|frameless|627x627px]] | |||
[[File:Palpation.jpg|right|frameless|427x427px]] | |||
* | === Neurological Assessment === | ||
==== Upper Extremity Nerve Palpation: ==== | |||
Goal is to reproduce symptoms if a peripheral nerve entrapment diagnosis is suspected.<ref>Schmid AB, Brunner F, Luomajoki H, et al. Reliability of clinical tests to evaluate nerve function and mechanosensitivity of the upper limb peripheral nervous system. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009;10:11.</ref> | |||
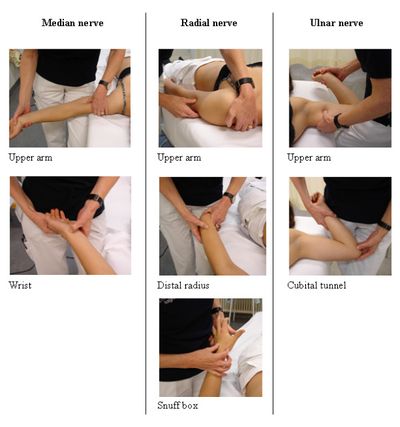
To palpate the 3 major nerves of the upper extremity refer to the figure below. | To palpate the 3 major nerves of the upper extremity refer to the figure below. | ||
* [[Median Nerve|Median]]: Position patient supine, 90 degrees of shoulder abduction and elbow extension. Palpate medially to the bicep (mid humeral). Palpate distally at wrist. | |||
* [[Radial Nerve|Radial]]: Upper arm (0 degrees of abduction, palpate proximal to the lateral epicondyle), distal radius, and snuffbox | |||
* [[Ulnar Nerve|Ulnar]]: Upper arm (medial mid humeral area, shoulder 90 degrees of abduction, elbow 120 degrees of flexion) and cubital tunnel | |||
[[Reflexes]] - C5-C7 | |||
[[Myotomes]] - C5-T1 | |||
[[ | [[Dermatomes]] - C5-T1 | ||
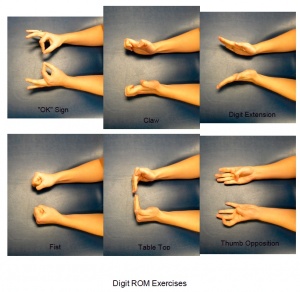
=== Movement Testing === | === Movement Testing === | ||
[[File:Digit ROM Exercise Handout.jpg|right|frameless]] | |||
If patient is pain free to end range, the physical therapist may choose to apply overpressure. | If patient is pain free to end range, the physical therapist may choose to apply overpressure. | ||
* '''Wrist''' | |||
*# Flexion/Extension | |||
*# Radial/Ulnar deviation | |||
*'''1st CMC''' | |||
# | *#Extension | ||
# | *#Abduction | ||
*#Opposition | |||
* | * '''Metacarpal-phalangeal (MCP)''' | ||
*# Flexion | |||
*#Extension | |||
*#Abduction/Adduction | |||
* '''Inter-phalangeal (IP)/Distal IP/Proximal IP''' | |||
*# Flexion | |||
*#Extension | |||
Inter-phalangeal (IP)/Distal IP/Proximal IP | |||
#Flexion | |||
#Extension | |||
=== Strength Testing === | === Strength Testing === | ||
#Wrist flexion/extension | #Wrist flexion/extension | ||
#Forearm pronation and supination | #Forearm pronation and supination | ||
#Grip strength | #[[Grip Strength|Grip]] strength | ||
#Key and pinch grip strength | #Key and pinch grip strength | ||
| Line 150: | Line 166: | ||
The physical therapist may elect to perform various special tests during the physical examination of an individual with wrist or hand complaints. Below are potential tests that may be utilized categorized by possible diagnosis or tissue involvement. | The physical therapist may elect to perform various special tests during the physical examination of an individual with wrist or hand complaints. Below are potential tests that may be utilized categorized by possible diagnosis or tissue involvement. | ||
* [[Scaphoid Fracture]] clinical examination (Anatomical snuff box tenderness; Scaphoid tubercle tenderness; Axial loading of the thumb) | |||
[[ | * [[Neurodynamic Assessment|Neurodynamic]] tests | ||
** [https://physio-pedia.com/Neurodynamic_Assessment#share <nowiki>Median nerve bias (Upper limb tension test 1 [ULTT] /UpperLimb Tension Test 2a)</nowiki>] | |||
** [https://physio-pedia.com/Neurodynamic_Assessment#share Radial nerve bias (ULTT2b)] | |||
**[https://physio-pedia.com/Neurodynamic_Assessment#share Ulnar nerve bias (ULTT3)] | |||
[[ | * [[Carpal Tunnel Syndrome|Carpal tunnel syndrome]] (Carpal compression test[http://www.physio-pedia.com/index.php5?title=Tinel%E2%80%99s_Test ; Tinel’s test]; Wrist-ratio index) | ||
[http://www.physio-pedia.com/index.php5?title=Scapholunate_Dissociation Scapholunate instability] ([http://www.physio-pedia.com/index.php5?title=Scaphoid_%28Watson%29_Shift_Test Scaphoid Shift test]) | * [http://www.physio-pedia.com/index.php5?title=Scapholunate_Dissociation Scapholunate instability] ([http://www.physio-pedia.com/index.php5?title=Scaphoid_%28Watson%29_Shift_Test Scaphoid Shift test]) | ||
[[De Quervain's Tenosynovitis|DeQuervain’s]] syndrome<br> | * [[De Quervain's Tenosynovitis|DeQuervain’s]] syndrome ([[Finkelstein Test]])<br> | ||
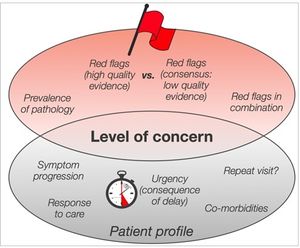
=== Red [[The Flag System|Flags]] === | === Red [[The Flag System|Flags]] === | ||
[[File:Red Flag Framework Level Concern.JPG|right|frameless]] | |||
This section deals with screening the patient for possible serious pathologies that could cause wrist or hand pain. These conditions could warrant a referral, or consultation. <br>'''Infections''' | This section deals with screening the patient for possible serious pathologies that could cause wrist or hand pain. These conditions could warrant a referral, or consultation. <br>'''Infections''' | ||
| Line 170: | Line 187: | ||
*Pain | *Pain | ||
*Redness | *Redness | ||
*Inflammation | *[[Inflammation Acute and Chronic|Inflammation]] | ||
'''Fracture/dislocation:''' | '''Fracture/dislocation:''' | ||
Top five physical findings which are most useful in screening for wrist fracture.<ref>Cevik AA, Gunal I, Manisali M, et al. Evaluation of physical findings in acute wrist trauma in the emergency department. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2003;9(4):257-261.</ref> | Top five physical findings which are most useful in screening for [[Colles Fracture|wrist fracture]].<ref>Cevik AA, Gunal I, Manisali M, et al. Evaluation of physical findings in acute wrist trauma in the emergency department. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2003;9(4):257-261.</ref> - Localized tenderness, Pain on active motion, Pain on passive motion, Pain on grip, Pain on supination | ||
Anyone of the above findings associated with a history of trauma should be sent for radiographs | |||
<u>Additional potentially serious conditions </u> | |||
*[[Scapholunate Dissociation|Scapholunate instability]] | *[[Scapholunate Dissociation|Scapholunate instability]] | ||
* | *Arthritides | ||
*[[Rheumatoid Arthritis]] | *[[Rheumatoid Arthritis]] | ||
*[[Lyme Disease|Lyme disease]] | *[[Lyme Disease|Lyme disease]] | ||
| Line 194: | Line 203: | ||
*Peripheral Vascular Disease | *Peripheral Vascular Disease | ||
*Peripheral Neuropathy | *Peripheral Neuropathy | ||
* | *History of trauma, fall on outstretched hand (FOOSH). Older age >65. The risk is same for men/women | ||
*Upper extremity nerve injuries involving :[[Median Nerve|Median]]; [[Radial nerve|Radial]]; [[Ulnar Nerve|Ulnar]] | *Upper extremity nerve injuries involving:[[Median Nerve|Median]]; [[Radial nerve|Radial]]; [[Ulnar Nerve|Ulnar]] | ||
== | == Possible Diagnosis Examples from Examination == | ||
* [[Carpal Tunnel Syndrome]] | * [[Carpal Tunnel Syndrome]] | ||
* Anterior Interosseous Syndrome | * Anterior Interosseous Syndrome | ||
* [[Posterior | * [[Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome|Posterior Interosseus Syndrome]] | ||
* [[Distal Radial Fractures]] | * [[Distal Radial Fractures]] | ||
* [[Osteoarthritis]] | * [[Osteoarthritis]] | ||
| Line 217: | Line 226: | ||
*[[DASH Outcome Measure|DASH:]] | *[[DASH Outcome Measure|DASH:]] | ||
*[[Grip Strength]], functional test. | |||
*Quick DASH | *Quick DASH | ||
*Symptom Severity Scale | *Symptom Severity Scale | ||
*[[Patient Specific Functional Scale]] | *[[Patient Specific Functional Scale]] | ||
== | == Conclusion == | ||
< | Hand and wrist complaints are common presentations to physiotherapy clinics. Some practices are special "hand" clinics. Being able to perform a thorough examination is vital. Common acute problems include fractures, tendonitis, and trigger finger. | ||
* Common chronic problems include [[Carpal Tunnel Syndrome|carpal tunnel syndrome]], ganglions and [[arthritis]]. | |||
* There are two conditions commonly examined – [[osteoarthritis]] and [[Hand Rheumatoid Arthritis|rheumatoid arthritis]] (be familiar with the changes that each of these conditions can cause).<ref>Medistudents [https://www.medistudents.com/en/learning/osce-skills/musculoskeletal/hand-wrist-examination/ Wrist and hand examination] Available from:https://www.medistudents.com/en/learning/osce-skills/musculoskeletal/hand-wrist-examination/ (last accessed 29.3.2020)</ref> | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Assessment]] | [[Category:Assessment]] | ||
[[Category:Wrist | [[Category:Wrist - Assessment and Examination]] | ||
[[Category:Wrist]] | [[Category:Wrist]] | ||
[[Category:Hand]] | [[Category:Hand]] | ||
| Line 236: | Line 248: | ||
[[Category:Sports Medicine]] | [[Category:Sports Medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Athlete Assessment]] | [[Category:Athlete Assessment]] | ||
[[Category:Hand - Assessment and Examination]] | |||
[[Category:Hand - Conditions]] | |||
Latest revision as of 02:26, 28 January 2023
Original Editor - Adam Ruff and Christian Filer as part of the Temple University EBP Project
Top Contributors - Christian Filer, Lucinda hampton, Kim Jackson, Admin, Rachael Lowe, Anas Mohamed, Laura Ritchie, Kai A. Sigel, Shaimaa Eldib, Tony Lowe, Alan Jit Ho Mak, Claire Knott, Scott A Burns, Temitope Olowoyeye, Evan Thomas, Scott Buxton, Naomi O'Reilly, WikiSysop, Fasuba Ayobami, Vidya Acharya, Wanda van Niekerk and Adam Ruff
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The hand and wrist form a group of complex, delicately balanced joints which are considered the most active portion of the upper extremity. Optimal overall function is important to so many activities of daily living. A hand and wrist examination done in a structured manner will help to facilitate the most appropriate working diagnosis for treatment. Diagnosing hand and wrist conditions is often difficult and for this reason, bilateral comparison can be useful[1]
Subjective History[edit | edit source]
Thorough history taking is an important first step in treating the patient. Each physical therapist will develop their own style and technique, but a good interview will include the basic elements discussed below:
- Mechanism of the injury - How the injury occurred and what was the cause e.g. fall on an outstretched hand
- Insidious or sudden injury.
- Handedness, occupation, previous injury and fracture history
- Location of the pain
- Presence and location of numbness, pins and needles and/or tingling.
- Aggravating and relieving factors.
- Functional limitations.
- Were any diagnostic test/imaging performed and what were the results?
Objective Examination[edit | edit source]
Screen Proximal Joints[edit | edit source]
Screen proximal structures to determine if they are involved in the patient’s clinical presentation. i.e. Cervical joints, Shoulder, Elbow.
Observation[edit | edit source]
Start by watching this 8 minute video of a wrist and hand examination.
- Observe upper extremity as the patient enters the room
- Examine hand in function
- Deformities
- Attitude of the hand
- Palmar Surface
- Creases
- Thenar and Hypothenar Eminence
- Arched Framework
- Hills and Valleys
- Dorsal surface
- Hills and Valleys
- Height of metacarpal heads
- Deformities.
- Ganglions - Cystic structure that arises from synovial sheath
- Boutonniere Deformity
- Swan Neck Deformity (see image)
- Osteoarthritis - Heberden’s nodes: DIP, Bouchard’s nodes: PIP
- Dupuytren’s Contractures
- Rheumatoid Arthritis - MCP swelling, Swan neck deformities, Ulnar deviation at MCP joints, Nodules along tendon sheaths.[1] (see R)
- Muscle wasting due to nerve dysfunction
- Median Nerve (depending on area impingement)
- Muscle wasting in the thenar eminence, first three fingers, and half the fourth fingers on radial side of the hand.
- Radial Nerve (depending on area of impingement)
- Common muscles that are affected by radial nerve entrapment are primarily on the dorsal aspect of the hand.
- Ulnar Nerve (depending on area of impingement)
- Muscle wasting in the hand for the ulnar nerve occurs primarily in the fifth and half the fourth fingers, in the hypothenar area.
Functional Tests[edit | edit source]
Goals - to obtain and quantify an asterisk to assess/reassess after the intervention is performed, for example: turning doorknob, holding a key, initial pain-free grip or key grip, opening a jar, turning on tap, lifting saucepan. Grip strength can also be a good reliable tool to use (available cheaply on internet).
Palpation[edit | edit source]
Wrist (Dorsal to Volar)
- Radial Styloid
- Scaphoid
- 1st MC/Trapezium joints
- Lunate
- Lister’s Tubercle
- Ulnar Styloid
- TFCC
- Triquetrum
- Pisiform
- Hook of Hamate
- Guyon’s Tunnel[1]
Palpation of Hand
- Bone
- Metacarpals - 5, Phalanges - 14, (Palpate for swelling, tenderness)
- Soft tissues
- 6 Dorsal Compartments – Transport extensor tendons See image at R
1st compartment- De quervains 2nd compartment - Intersection syndrome
| Compartment 1 (Most radial) | Compartment 2 | Compartment 3 | Compartment 4 | Compartment 5 | Compartment 6 (Most ulnar) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abductor pollicis longus | Extensor carpi radialis longus | Extensor pollicis longus | Extensor indicis | Extensor digiti minimi | Extensor carpi ulnaris |
| Extensor pollicis brevis | Extensor carpi radialis brevis | Extensor digitorum communis |
2 Palmar Tunnels – Transport nerves, arteries, flexor tendons
Palmar Aspect - Pisiform and Hamate, Tunnel of Guyon, Carpal Tunnel, Flexor Carpi Radialis, Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Palm of Hand
- Thenar Eminence (3 muscles of thumb, Atrophy seen in carpal tunnel syndrome)
- Hypothenar Eminance (3 muscles of little finger, Atrophy with ulnar nerve compression)
- Palmar Aponeurosis (Dupuytren’s Contracture)[1]
Neurological Assessment[edit | edit source]
Upper Extremity Nerve Palpation:[edit | edit source]
Goal is to reproduce symptoms if a peripheral nerve entrapment diagnosis is suspected.[4]
To palpate the 3 major nerves of the upper extremity refer to the figure below.
- Median: Position patient supine, 90 degrees of shoulder abduction and elbow extension. Palpate medially to the bicep (mid humeral). Palpate distally at wrist.
- Radial: Upper arm (0 degrees of abduction, palpate proximal to the lateral epicondyle), distal radius, and snuffbox
- Ulnar: Upper arm (medial mid humeral area, shoulder 90 degrees of abduction, elbow 120 degrees of flexion) and cubital tunnel
Reflexes - C5-C7
Myotomes - C5-T1
Dermatomes - C5-T1
Movement Testing[edit | edit source]
If patient is pain free to end range, the physical therapist may choose to apply overpressure.
- Wrist
- Flexion/Extension
- Radial/Ulnar deviation
- 1st CMC
- Extension
- Abduction
- Opposition
- Metacarpal-phalangeal (MCP)
- Flexion
- Extension
- Abduction/Adduction
- Inter-phalangeal (IP)/Distal IP/Proximal IP
- Flexion
- Extension
Strength Testing[edit | edit source]
- Wrist flexion/extension
- Forearm pronation and supination
- Grip strength
- Key and pinch grip strength
Special Tests[edit | edit source]
The physical therapist may elect to perform various special tests during the physical examination of an individual with wrist or hand complaints. Below are potential tests that may be utilized categorized by possible diagnosis or tissue involvement.
- Scaphoid Fracture clinical examination (Anatomical snuff box tenderness; Scaphoid tubercle tenderness; Axial loading of the thumb)
- Neurodynamic tests
- Carpal tunnel syndrome (Carpal compression test; Tinel’s test; Wrist-ratio index)
- DeQuervain’s syndrome (Finkelstein Test)
Red Flags[edit | edit source]
This section deals with screening the patient for possible serious pathologies that could cause wrist or hand pain. These conditions could warrant a referral, or consultation.
Infections
- Heat
- Swelling
- Pain
- Redness
- Inflammation
Fracture/dislocation:
Top five physical findings which are most useful in screening for wrist fracture.[5] - Localized tenderness, Pain on active motion, Pain on passive motion, Pain on grip, Pain on supination
Anyone of the above findings associated with a history of trauma should be sent for radiographs
Additional potentially serious conditions
- Scapholunate instability
- Arthritides
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Tuberculosis
- Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- History of trauma, fall on outstretched hand (FOOSH). Older age >65. The risk is same for men/women
- Upper extremity nerve injuries involving:Median; Radial; Ulnar
Possible Diagnosis Examples from Examination[edit | edit source]
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Anterior Interosseous Syndrome
- Posterior Interosseus Syndrome
- Distal Radial Fractures
- Osteoarthritis
- First Carpometacarpal Osteoarthritis
- Hand and Wrist Osteoarthritis
- DeQuervain Syndrome
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome
- Compression of the Ulnar nerve at Guyon’s canal
- Non-specific wrist pain (mechanical wrist pain)
- Trigger Finger
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
- Triangular Fibrocartilaginous Complex
- Dupuytren’s Contracture
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
- DASH:
- Grip Strength, functional test.
- Quick DASH
- Symptom Severity Scale
- Patient Specific Functional Scale
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
Hand and wrist complaints are common presentations to physiotherapy clinics. Some practices are special "hand" clinics. Being able to perform a thorough examination is vital. Common acute problems include fractures, tendonitis, and trigger finger.
- Common chronic problems include carpal tunnel syndrome, ganglions and arthritis.
- There are two conditions commonly examined – osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis (be familiar with the changes that each of these conditions can cause).[6]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Shane Cass, DO UNM Primary Care Sports Medicine Clinical Examination of the Hand and Wrist Available from:http://unmfm.pbworks.com/w/file/fetch/50237999/HandandWristExammaster.pdf
- ↑ Ascension Via Christi Joint-by-Joint Musculoskeletal Physical Exam: Hand and Wrist Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DxW0rodKOGs (last accessed 29.3.2020)
- ↑ Wikimedia commons Wrist extensor compartments Available from:https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Wrist_extensor_compartments_(numbered).PNG
- ↑ Schmid AB, Brunner F, Luomajoki H, et al. Reliability of clinical tests to evaluate nerve function and mechanosensitivity of the upper limb peripheral nervous system. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009;10:11.
- ↑ Cevik AA, Gunal I, Manisali M, et al. Evaluation of physical findings in acute wrist trauma in the emergency department. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2003;9(4):257-261.
- ↑ Medistudents Wrist and hand examination Available from:https://www.medistudents.com/en/learning/osce-skills/musculoskeletal/hand-wrist-examination/ (last accessed 29.3.2020)