Forward Head Posture: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(text, refs, format, images) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Forward Head Posture - affects on Health == | == Forward Head Posture - affects on Health == | ||
FHP evaluation is clinically important for diagnosis and rehabilitation treatment. [[File:Code-ninja-DThlV4dYlnE-unsplash (1).jpg|right|frameless]]FHP increases compressive loading on tissues in the cervical spine, particularly the facet joints and ligaments. | FHP evaluation is clinically important for diagnosis and rehabilitation treatment. [[File:Code-ninja-DThlV4dYlnE-unsplash (1).jpg|right|frameless]] | ||
* FHP increases compressive loading on tissues in the cervical spine, particularly the facet joints and ligaments. | |||
Studies have reported that symptoms including neck pain, headache, temporomandibular pain, and musculoskeletal disorders are related to FHP | * Studies have reported that symptoms including neck pain, headache, temporomandibular pain, and musculoskeletal disorders are related to FHP | ||
* FHP greatly influences respiratory function by weakening the respiratory muscles<ref name=":3" />. | |||
FHP greatly influences respiratory function by weakening the respiratory muscles<ref name=":3" />. | * Forward head and round-shoulder postures (FHRSP) can result in shoulder pain and dysfunction because of altered scapular kinematics and muscle activity and consequently, placing increased stress on the shoulder.<ref>Fathollahnejad K, Letafatkar A, Hadadnezhad M. [https://bmcmusculoskeletdisord.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12891-019-2438-y The effect of manual therapy and stabilizing exercises on forward head and rounded shoulder postures: a six-week intervention with a one-month follow-up study.] BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2019 Dec 1;20(1):86.Available from:https://bmcmusculoskeletdisord.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12891-019-2438-y</ref><ref name=":4">Burt HA, [https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/003591575004300315 Effects of faulty posture; President's Address]. Proc R Soc Med. 1950; 43(3):187–194. Accessed 26 February 2019. | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
* In the posterior cervical muscles there is stretching and weakness of [[Semispinalis Cervicis|Semispinalis cervicis]] and overaction with ultimate shortening of [[Semispinalis Capitis|Semispinalis capitis]]. The corresponding flexor muscles in front, namely, [[Longus Colli|Longus cervicis]] and [[Longus Capitis|Longus capitis]] shorten and lengthen respectively.<ref name=":4" /> | |||
== Eitiology == | |||
== | |||
* Occupational posture: forward or backward leaning of head for long durations, slouched or relaxed sitting, faulty sitting posture while using computer or screen. | * Occupational posture: forward or backward leaning of head for long durations, slouched or relaxed sitting, faulty sitting posture while using computer or screen. | ||
* | * Effect of gravity: slouching, poor ergonomic alignment. | ||
* Other faulty postures like pelvic and lumber spine posture. | |||
* Sleeping with head elevated too high. | * Sleeping with head elevated too high. | ||
* | * Poor posture maintained for long durations. | ||
*Lack of development of back muscle strength. | *Lack of development of back muscle strength. | ||
== | === Clinical Findings === | ||
* | Include | ||
* Muscle ischaemia, pain and fatigue[[File:Head 1.jpg|right|frameless|400x400px]] | |||
* Decreased range of motion of cervical spine<ref>Kim DH, Kim CJ, Son SM. Neck pain in adults with forward head posture: effects of craniovertebral angle and cervical range of motion. Osong public health and research perspectives. 2018 Dec;9(6):309.</ref> | * Decreased range of motion of cervical spine<ref>Kim DH, Kim CJ, Son SM. Neck pain in adults with forward head posture: effects of craniovertebral angle and cervical range of motion. Osong public health and research perspectives. 2018 Dec;9(6):309.</ref> | ||
* Early disc degeneration and osteophyte formation | * Early disc degeneration and osteophyte formation | ||
| Line 56: | Line 47: | ||
* Possible protrusion of nucleus pulposus and nerve compression | * Possible protrusion of nucleus pulposus and nerve compression | ||
* Mobility impairment in the muscles of the anterior thorax (intercostal muscles), muscles of the upper extremity <ref>Weon JH, Oh JS, Cynn HS, Kim YW, Kwon OY, Yi CH. Influence of forward head posture on scapular upward rotators during isometric shoulder flexion. Journal of Bodywork and movement therapies. 2010 Oct 1;14(4):367-74.</ref>originating on the thorax ([[Pectoralis major]] et [[Pectoralis Minor|minor]], [[Latissimus Dorsi Muscle|Latissimus dorsi]], [[Serratus Anterior|Serratus anterior]]), muscles of the cervical spine and head that attached to the [[scapula]] and upper thorax ([[Levator Scapulae|Levator scapulae]], [[Sternocleidomastoid]], [[Scalene]], [[Trapezius|upper Trapezius]]), and muscles of the suboccipital region ([[Rectus Capitis Anterior|Rectus capitis]] [[Rectus Capitis Posterior Major|posterior major]] and [[Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor|minor]], [[Obliquus Capitis Inferior|Obliquus capitis inferior]] and [[Obliquus Capitis Superior|superior]]). | |||
* Mobility impairment in the muscles of the anterior thorax (intercostal muscles), muscles of the upper extremity <ref>Weon JH, Oh JS, Cynn HS, Kim YW, Kwon OY, Yi CH. Influence of forward head posture on scapular upward rotators during isometric shoulder flexion. Journal of Bodywork and movement therapies. 2010 Oct 1;14(4):367-74.</ref>originating on the thorax ([[Pectoralis major]] | |||
* Impaired muscle performance due to stretched and weak lower cervical and upper thoracic erector spinae and scapular retractor muscles ([[Rhomboids]], middle [[Trapezius]]), anterior throat muscles (suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles), and capital flexors ([[Rectus Capitis Anterior|Rectus capitis anterior]] and [[Rectus Capitis Lateralis|lateralis]], [[Longus Colli|superior oblique Longus colli]], [[Longus Capitis|Longus capitis]]). | * Impaired muscle performance due to stretched and weak lower cervical and upper thoracic erector spinae and scapular retractor muscles ([[Rhomboids]], middle [[Trapezius]]), anterior throat muscles (suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles), and capital flexors ([[Rectus Capitis Anterior|Rectus capitis anterior]] and [[Rectus Capitis Lateralis|lateralis]], [[Longus Colli|superior oblique Longus colli]], [[Longus Capitis|Longus capitis]]). | ||
* With temporomandibular joint symptoms, the muscles of mastication may have increased tension (Pterygoid, Masseter, temporalis muscles).<ref name=":1">Kisner C, Colby LA. Therapeutic Exercises. Fifth Edition. USA: F.A. Davis Company.2007. p384-404. | * With temporomandibular joint symptoms, the muscles of mastication may have increased tension (Pterygoid, Masseter, temporalis muscles).<ref name=":1">Kisner C, Colby LA. Therapeutic Exercises. Fifth Edition. USA: F.A. Davis Company.2007. p384-404. | ||
</ref> | </ref><ref name=":2">Levangie PK, Norkin CC. Joint Structure and Function. Fifth Edition. USA: F.A. Davis Company. 2011. p501-37 | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
== Physiotherapy Management == | == Physiotherapy Management == | ||
* ''To Decrease Pain:'' | * ''To Decrease Pain:'' [[File:Ergonomics .png|''Source: Yamavu Author: Yamavu Permission: Universal public domain'' |right|frameless]] | ||
*# Pain management advice | *# [[Chronic Pain|Pain management]] advice | ||
* ''Postural Alignment, Balance and Gait:'' | * ''Postural Alignment, [[Balance]] and [[Gait|Gait:]]'' | ||
*# Cervical Retraction | *# Cervical Retraction | ||
*# Scapular Retraction | *# Scapular Retraction | ||
| Line 79: | Line 65: | ||
*# Shoulder Range of Motion Exercises | *# Shoulder Range of Motion Exercises | ||
*# Cervical Traction | *# Cervical Traction | ||
*# [[Thoracic Manual Techniques and Exercises|Thoracic Manual Techniques and exercises]] | |||
*# Stretching Exercises of tight structures- Trapezius, Scalenes, SCM, Pectoralis Major and Minor. | *# Stretching Exercises of tight structures- Trapezius, Scalenes, SCM, Pectoralis Major and Minor. | ||
* ''To reduce spasm '' | * ''To reduce spasm '' | ||
*# Myofacial release | *# [[Myofascial Release|Myofacial]] release | ||
*# Ischemic Compression | *# Ischemic Compression | ||
*# Positional release technique (to relieve tension headaches) | *# Positional release technique (to relieve tension headaches) | ||
| Line 93: | Line 80: | ||
** Correct the number of pillows used | ** Correct the number of pillows used | ||
** Postural corrections. | ** Postural corrections. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 08:17, 23 April 2020
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Because of the rising popularity of media devices such as smartphones and computers, frequent users often exhibit incorrect posture.
Forward head posture (FHP) is a poor habitual neck posture
- Defined by hyperextension of the upper cervical vertebrae and forward translation of the cervical vertebrae.[1]
- Thoracic Kyphosis is a complication of the combination of slouched-forward shoulders and rounded upper back.
- Can lead to a painful shortening of the muscles of the back of the neck, as well as compression of the cervical vertebrae—the uppermost portion of the spine that supports the head and protects the spinal cord.
Due to the increased compressive forces through the neck joints and increased muscle tension, pain is the common outcome. Some of the types of problems associated with FHP are:
- Headaches
- Neck discomfort
- Muscle tension in the neck and shoulders
- Discomfort in the mid back
- Chest pain
- Pain, pins & needles and numbness in the arms and hands
Many people develop chronic or recurrent problems because they receive treatment for the pain (e.g. pain killers or anti-inflammatory medication) but never receive treatment for the underlying cause which is their FHP.[2]
Forward Head Posture - affects on Health[edit | edit source]
FHP evaluation is clinically important for diagnosis and rehabilitation treatment.
- FHP increases compressive loading on tissues in the cervical spine, particularly the facet joints and ligaments.
- Studies have reported that symptoms including neck pain, headache, temporomandibular pain, and musculoskeletal disorders are related to FHP
- FHP greatly influences respiratory function by weakening the respiratory muscles[1].
- Forward head and round-shoulder postures (FHRSP) can result in shoulder pain and dysfunction because of altered scapular kinematics and muscle activity and consequently, placing increased stress on the shoulder.[3][4]
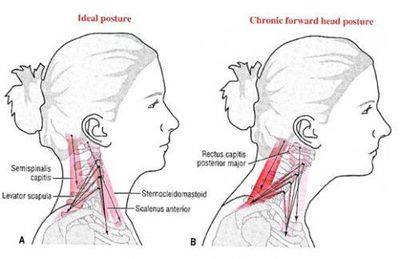
- In the posterior cervical muscles there is stretching and weakness of Semispinalis cervicis and overaction with ultimate shortening of Semispinalis capitis. The corresponding flexor muscles in front, namely, Longus cervicis and Longus capitis shorten and lengthen respectively.[4]
Eitiology[edit | edit source]
- Occupational posture: forward or backward leaning of head for long durations, slouched or relaxed sitting, faulty sitting posture while using computer or screen.
- Effect of gravity: slouching, poor ergonomic alignment.
- Other faulty postures like pelvic and lumber spine posture.
- Sleeping with head elevated too high.
- Poor posture maintained for long durations.
- Lack of development of back muscle strength.
Clinical Findings[edit | edit source]
Include
- Muscle ischaemia, pain and fatigue
- Decreased range of motion of cervical spine[5]
- Early disc degeneration and osteophyte formation
- Temporomandibular joint pain and inflammation
- Tension Headache
- Increase in dorsal kyphosis and decrease in height
- Decrease in vital capacity and range of motion of shoulder and arm
- Possible protrusion of nucleus pulposus and nerve compression
- Mobility impairment in the muscles of the anterior thorax (intercostal muscles), muscles of the upper extremity [6]originating on the thorax (Pectoralis major et minor, Latissimus dorsi, Serratus anterior), muscles of the cervical spine and head that attached to the scapula and upper thorax (Levator scapulae, Sternocleidomastoid, Scalene, upper Trapezius), and muscles of the suboccipital region (Rectus capitis posterior major and minor, Obliquus capitis inferior and superior).
- Impaired muscle performance due to stretched and weak lower cervical and upper thoracic erector spinae and scapular retractor muscles (Rhomboids, middle Trapezius), anterior throat muscles (suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles), and capital flexors (Rectus capitis anterior and lateralis, superior oblique Longus colli, Longus capitis).
- With temporomandibular joint symptoms, the muscles of mastication may have increased tension (Pterygoid, Masseter, temporalis muscles).[7][8]
Physiotherapy Management[edit | edit source]
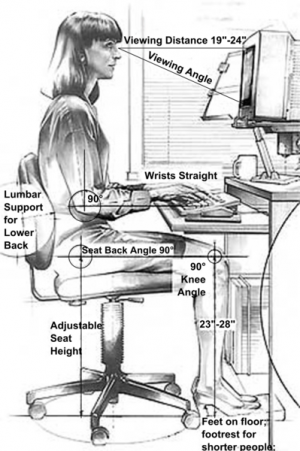
- To Decrease Pain:
- Pain management advice
- Postural Alignment, Balance and Gait:
- Cervical Retraction
- Scapular Retraction
- Balance Training ( If dysfunction presents)
- Range of Motion, Joint Mobility and Flexibility[9]
- Cervical Range of Motion Exercises
- Shoulder Range of Motion Exercises
- Cervical Traction
- Thoracic Manual Techniques and exercises
- Stretching Exercises of tight structures- Trapezius, Scalenes, SCM, Pectoralis Major and Minor.
- To reduce spasm
- Myofacial release
- Ischemic Compression
- Positional release technique (to relieve tension headaches)
- Muscle Strength and Endurance
- Cervical isometric strengthening exercises (initial phase) progressing to isotonic and dynamic strengtening exercises.
- Strengthening exercises for scapular retractors (Rhomboids, middle Trapezius).[10]
- Ergonomic Advice
- Correct the number of pillows used
- Postural corrections.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Koseki T, Kakizaki F, Hayashi S, Nishida N, Itoh M. Effect of forward head posture on thoracic shape and respiratory function. Journal of physical therapy science. 2019;31(1):63-8. Available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?cmd=link&linkname=pubmed_pubmed_reviews&uid=30774207&log$=relatedreviews&logdbfrom=pmc (last accessed 23.4.2020)
- ↑ Centralcity Health professionals FHP Available from:https://www.centralcityphysio.com.au/forward-head-posture/ (last accessed 23.4.2020)
- ↑ Fathollahnejad K, Letafatkar A, Hadadnezhad M. The effect of manual therapy and stabilizing exercises on forward head and rounded shoulder postures: a six-week intervention with a one-month follow-up study. BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2019 Dec 1;20(1):86.Available from:https://bmcmusculoskeletdisord.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12891-019-2438-y
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Burt HA, Effects of faulty posture; President's Address. Proc R Soc Med. 1950; 43(3):187–194. Accessed 26 February 2019.
- ↑ Kim DH, Kim CJ, Son SM. Neck pain in adults with forward head posture: effects of craniovertebral angle and cervical range of motion. Osong public health and research perspectives. 2018 Dec;9(6):309.
- ↑ Weon JH, Oh JS, Cynn HS, Kim YW, Kwon OY, Yi CH. Influence of forward head posture on scapular upward rotators during isometric shoulder flexion. Journal of Bodywork and movement therapies. 2010 Oct 1;14(4):367-74.
- ↑ Kisner C, Colby LA. Therapeutic Exercises. Fifth Edition. USA: F.A. Davis Company.2007. p384-404.
- ↑ Levangie PK, Norkin CC. Joint Structure and Function. Fifth Edition. USA: F.A. Davis Company. 2011. p501-37
- ↑ Szczygieł E, Sieradzki B, Masłoń A, Golec J, Czechowska D, Węglarz K, Szczygieł R, Golec E. Assessing the impact of certain exercises on the spatial head posture. International journal of occupational medicine and environmental health. 2019 Feb 27;32(1):43-51.
- ↑ Im B, Kim Y, Chung Y, Hwang S. Effects of scapular stabilization exercise on neck posture and muscle activation in individuals with neck pain and forward head posture. Journal of physical therapy science. 2015;28(3):951-5.